portfolio
We’re helping CommBank shape the bank of the future, one venture at a time
There’s a blurring of industry lines happening everywhere. To meet customer needs and expectations, we have to look more broadly than just traditional products and services and really enrich the proposition in aggregate.
Stuart Munro
Group Head of Strategy, CommBank
Our ventures
We're helping CommBank reimagine what it means to be a bank, with products and services that improve people's lives in the moments that matter.
Built and owned
Home-in
2020
Home
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
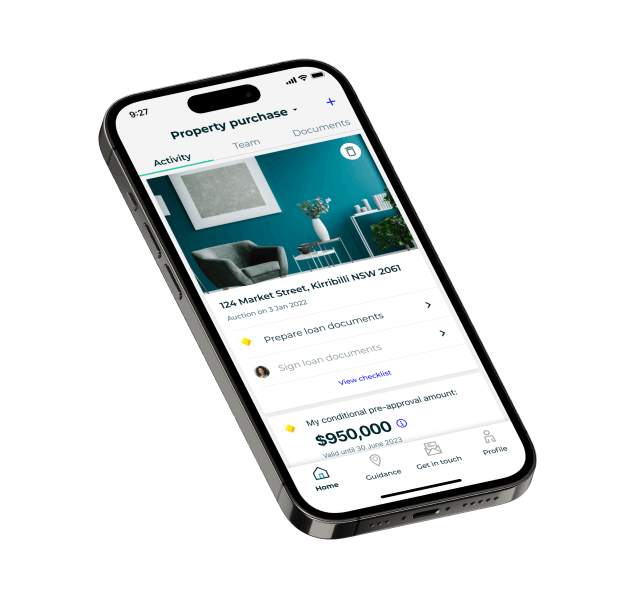

Home-in simplifies the complex process of buying a home. It helps buyers navigate the home buying journey and reach settlement with certainty.

Home-in simplifies the complex process of buying a home. It helps buyers navigate the home buying journey and reach settlement with certainty.
Home-in
2020
Home
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in
Home-in


Home-in simplifies the complex process of buying a home. It helps buyers navigate the home buying journey and reach settlement with certainty.

Home-in simplifies the complex process of buying a home. It helps buyers navigate the home buying journey and reach settlement with certainty.
CreditSavvy
2020
Everyday
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
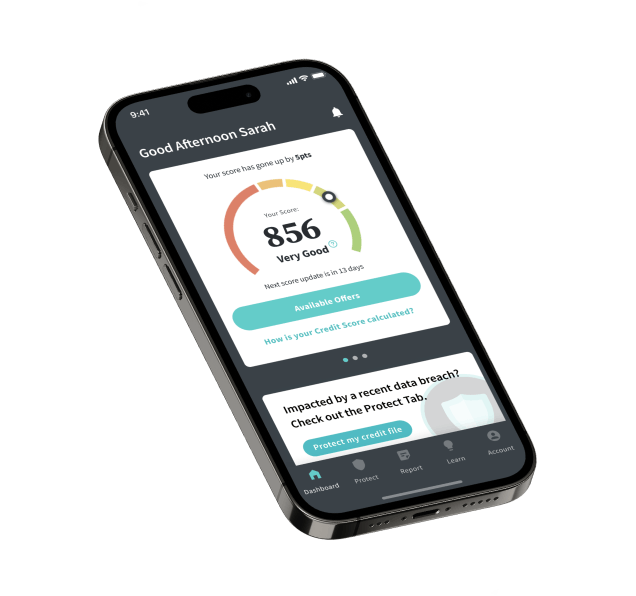

Credit Savvy helps Australians to access, understand and protect their credit reputation.

Credit Savvy helps Australians to access, understand and protect their credit reputation.
CreditSavvy
2020
Everyday
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy
CreditSavvy


Credit Savvy helps Australians to access, understand and protect their credit reputation.

Credit Savvy helps Australians to access, understand and protect their credit reputation.
Doshii
2021
Business
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
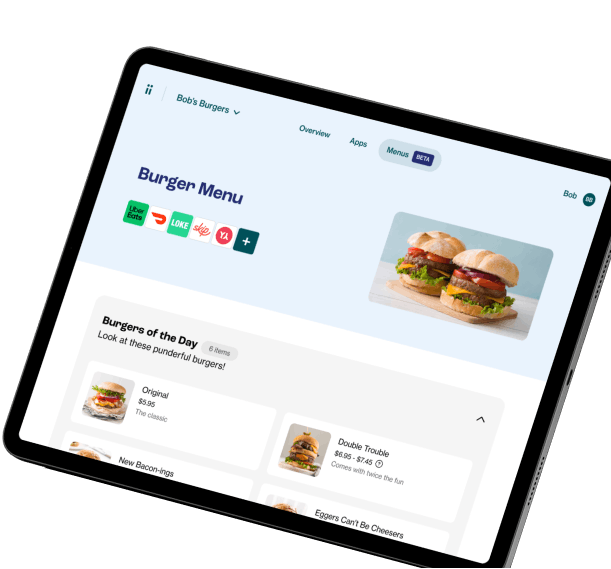

Doshii gets hospitality apps talking to a venue’s POS (point of sale platform), helping business owners spend less of their time on tech, and more on customers.

Doshii gets hospitality apps talking to a venue’s POS (point of sale platform), helping business owners spend less of their time on tech, and more on customers.
Doshii
2021
Business
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii
Doshii


Doshii gets hospitality apps talking to a venue’s POS (point of sale platform), helping business owners spend less of their time on tech, and more on customers.

Doshii gets hospitality apps talking to a venue’s POS (point of sale platform), helping business owners spend less of their time on tech, and more on customers.
Unloan
2022
Home
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan


Unloan is a new kind of home loan with one great rate, 10-minute application time, and a discount that gets better and better.

Unloan is a new kind of home loan with one great rate, 10-minute application time, and a discount that gets better and better.
Unloan
2022
Home
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan
Unloan


Unloan is a new kind of home loan with one great rate, 10-minute application time, and a discount that gets better and better.

Unloan is a new kind of home loan with one great rate, 10-minute application time, and a discount that gets better and better.
Kit
2022
Everyday
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
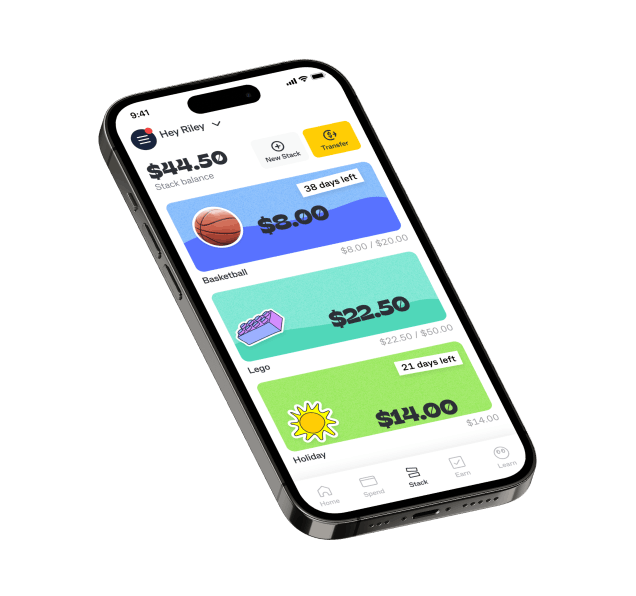

Kit is an earning-and-learning, mindfully-spending, money-mastering pocket money app and prepaid card, helping improve the financial capability of young people in Australia.

Kit is an earning-and-learning, mindfully-spending, money-mastering pocket money app and prepaid card, helping improve the financial capability of young people in Australia.
Kit
2022
Everyday
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit
Kit


Kit is an earning-and-learning, mindfully-spending, money-mastering pocket money app and prepaid card, helping improve the financial capability of young people in Australia.

Kit is an earning-and-learning, mindfully-spending, money-mastering pocket money app and prepaid card, helping improve the financial capability of young people in Australia.
Waddle
2023
Business
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
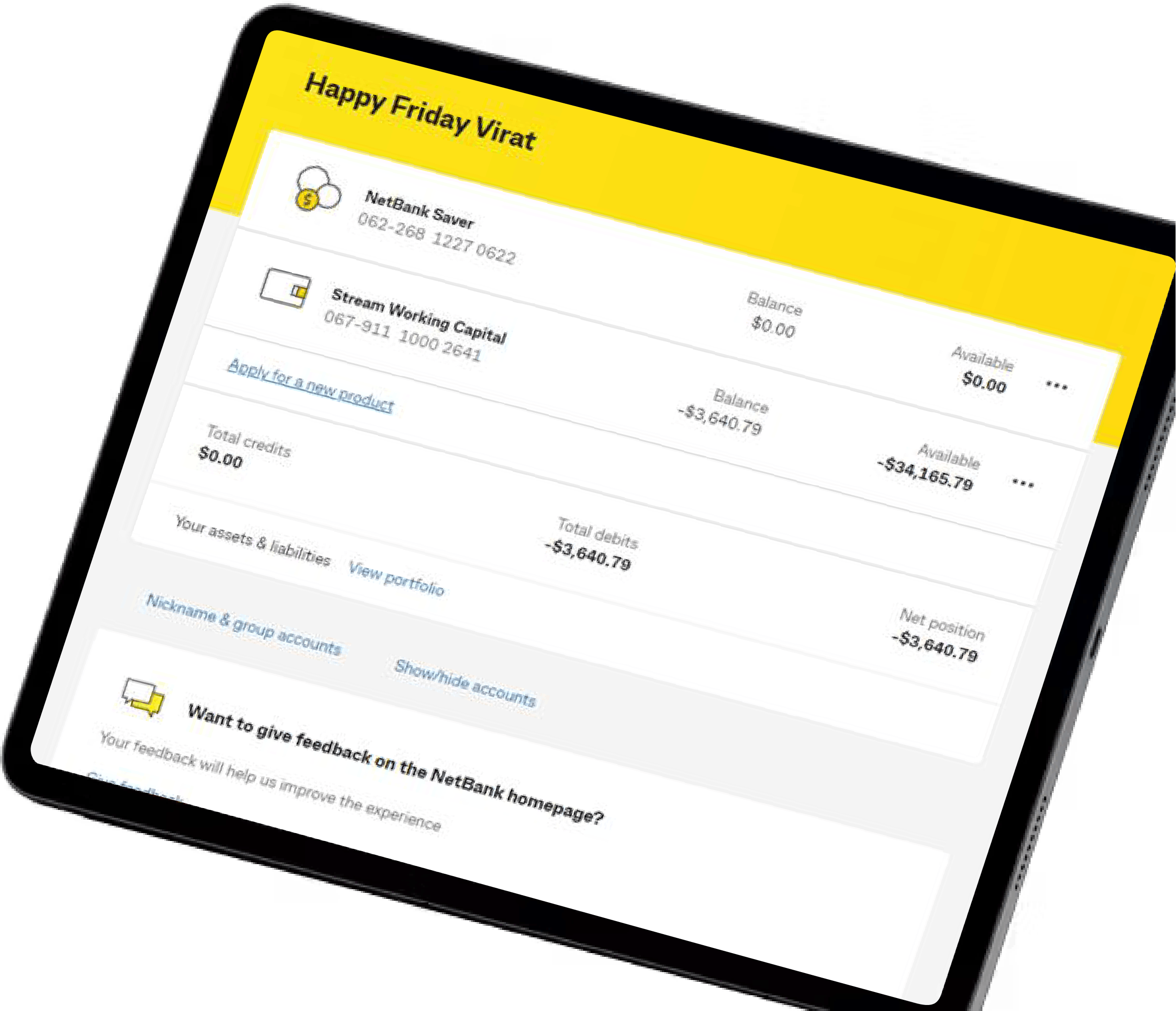

Waddle’s invoice lending platform powers CommBank's Stream Working Capital product, enabling small business owners to unlock cash tied up in unpaid invoices.

Waddle’s invoice lending platform powers CommBank's Stream Working Capital product, enabling small business owners to unlock cash tied up in unpaid invoices.
Waddle
2023
Business
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle
Waddle


Waddle’s invoice lending platform powers CommBank's Stream Working Capital product, enabling small business owners to unlock cash tied up in unpaid invoices.

Waddle’s invoice lending platform powers CommBank's Stream Working Capital product, enabling small business owners to unlock cash tied up in unpaid invoices.
Early-stage investments
Payble
2021
Everyday
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
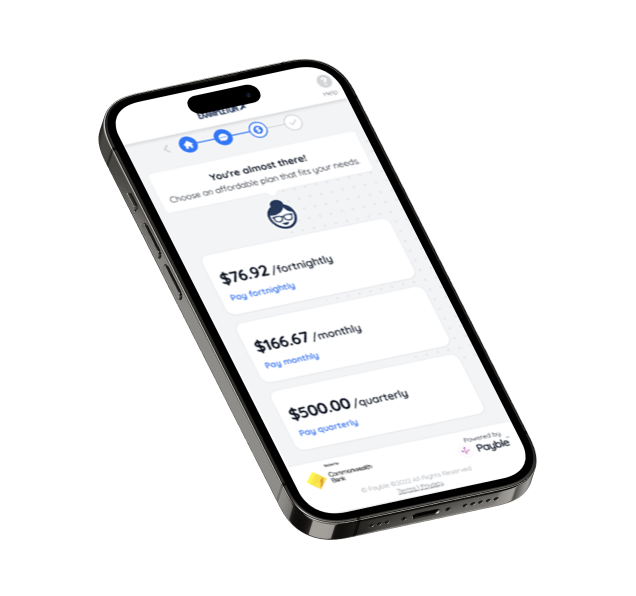

Payble is a citizen-centric revenue optimisation platform, helping governments improve revenue outcomes while delivering outstanding citizen payment experiences.

Payble is a citizen-centric revenue optimisation platform, helping governments improve revenue outcomes while delivering outstanding citizen payment experiences.
Payble
2021
Everyday
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble
Payble


Payble is a citizen-centric revenue optimisation platform, helping governments improve revenue outcomes while delivering outstanding citizen payment experiences.

Payble is a citizen-centric revenue optimisation platform, helping governments improve revenue outcomes while delivering outstanding citizen payment experiences.
Xccelerate investments
OwnHome
2020
Home
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome


Saving for a deposit is one of the main barriers for potential home buyers. OwnHome is a new pathway to homeownership, without the high upfront costs.

Saving for a deposit is one of the main barriers for potential home buyers. OwnHome is a new pathway to homeownership, without the high upfront costs.
OwnHome
2020
Home
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome
OwnHome


Saving for a deposit is one of the main barriers for potential home buyers. OwnHome is a new pathway to homeownership, without the high upfront costs.

Saving for a deposit is one of the main barriers for potential home buyers. OwnHome is a new pathway to homeownership, without the high upfront costs.
Splashup
2021
Business
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
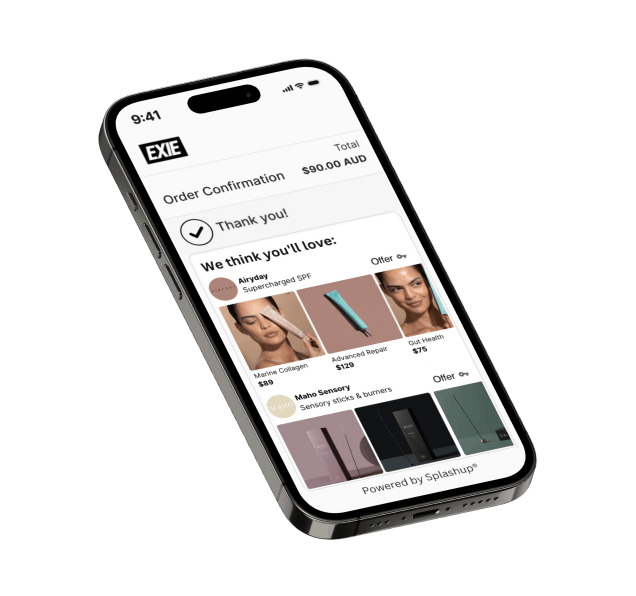

Splashup is an AI-driven partnerships platform, building a network of eCommerce merchants with post-transaction discovery experiences for high-intent shoppers.

Splashup is an AI-driven partnerships platform, building a network of eCommerce merchants with post-transaction discovery experiences for high-intent shoppers.
Splashup
2021
Business
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup
Splashup


Splashup is an AI-driven partnerships platform, building a network of eCommerce merchants with post-transaction discovery experiences for high-intent shoppers.

Splashup is an AI-driven partnerships platform, building a network of eCommerce merchants with post-transaction discovery experiences for high-intent shoppers.
Paytron
2022 (exited 2023)
Business
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
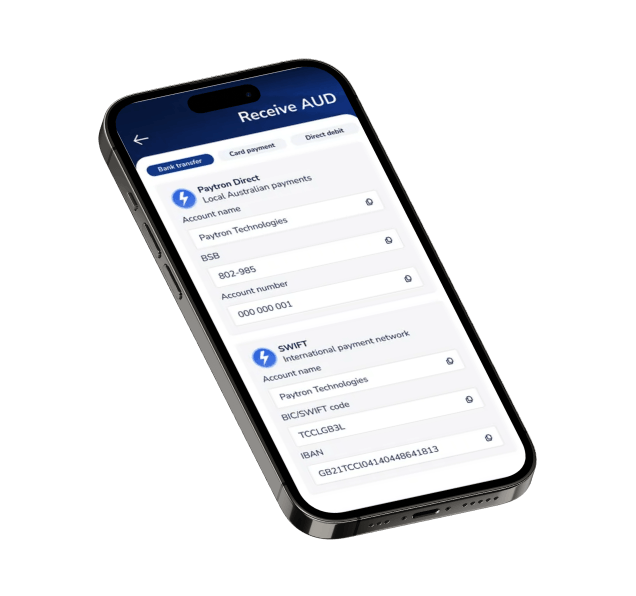

Paytron is a payment automation and spend management platform, simplifying the way finance teams manage transactions without a single line of code.

Paytron is a payment automation and spend management platform, simplifying the way finance teams manage transactions without a single line of code.
Paytron
2022 (exited 2023)
Business
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron
Paytron


Paytron is a payment automation and spend management platform, simplifying the way finance teams manage transactions without a single line of code.

Paytron is a payment automation and spend management platform, simplifying the way finance teams manage transactions without a single line of code.
Pairtree
2023
Business
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
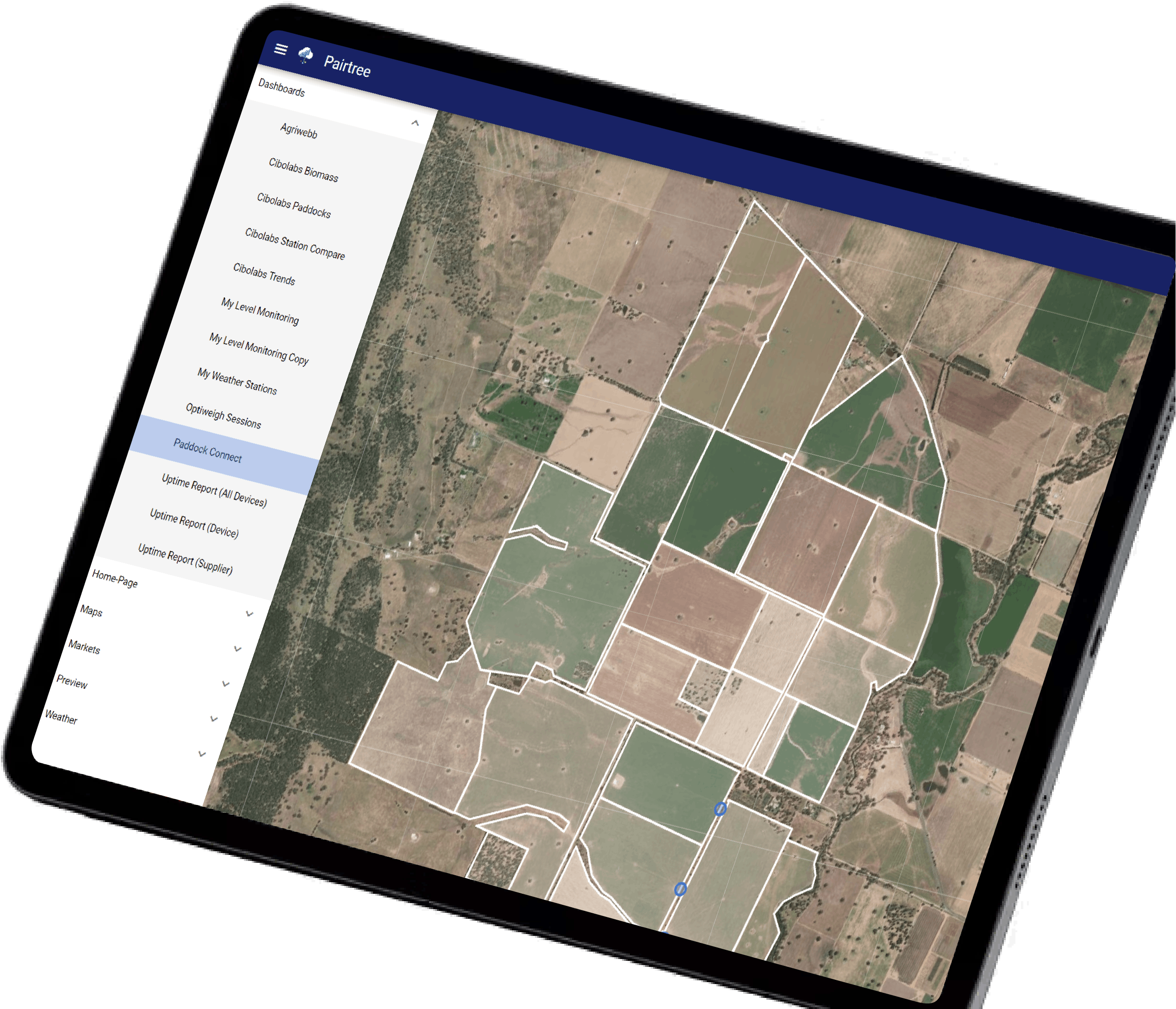

Pairtree reduces complexity for farmers by centralising 100+ sources of agricultural data into a single platform.

Pairtree reduces complexity for farmers by centralising 100+ sources of agricultural data into a single platform.
Pairtree
2023
Business
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree
Pairtree


Pairtree reduces complexity for farmers by centralising 100+ sources of agricultural data into a single platform.

Pairtree reduces complexity for farmers by centralising 100+ sources of agricultural data into a single platform.
Closed ventures
Unfortunately, not all startups reach scale, and the following ventures have closed:
Vonto
2020-2022
Business
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
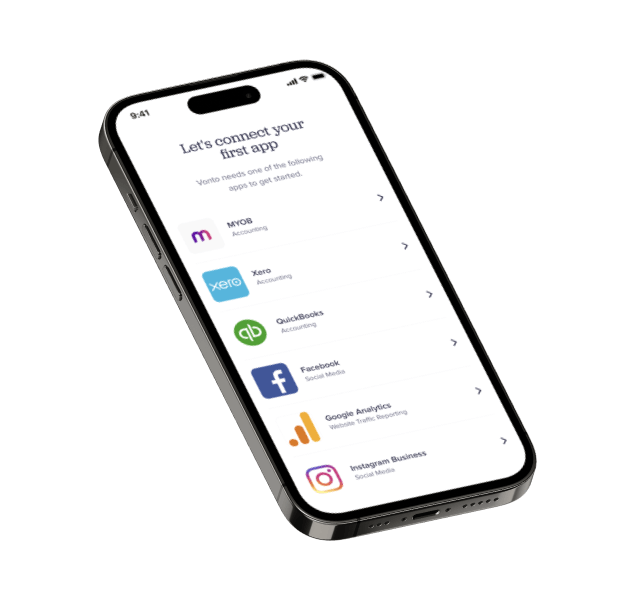

Vonto provided businesses with a feed of useful insights and information they could act on immediately.

Vonto provided businesses with a feed of useful insights and information they could act on immediately.
Vonto
2020-2022
Business
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto
Vonto


Vonto provided businesses with a feed of useful insights and information they could act on immediately.

Vonto provided businesses with a feed of useful insights and information they could act on immediately.
Backr
2020-2022
Business
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
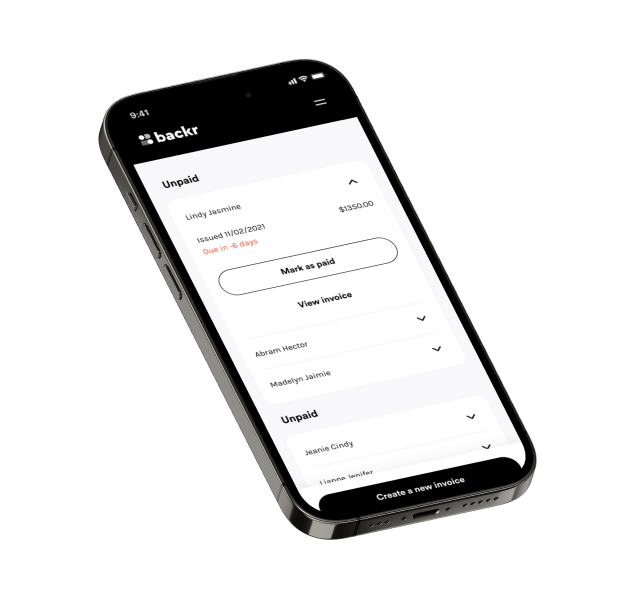

Backr was a digital platform for first-time business owners, which streamlined the process of setting up a business in Australia.

Backr was a digital platform for first-time business owners, which streamlined the process of setting up a business in Australia.
Backr
2020-2022
Business
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr
Backr


Backr was a digital platform for first-time business owners, which streamlined the process of setting up a business in Australia.

Backr was a digital platform for first-time business owners, which streamlined the process of setting up a business in Australia.
Cheddar
2021-2023
Everyday
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
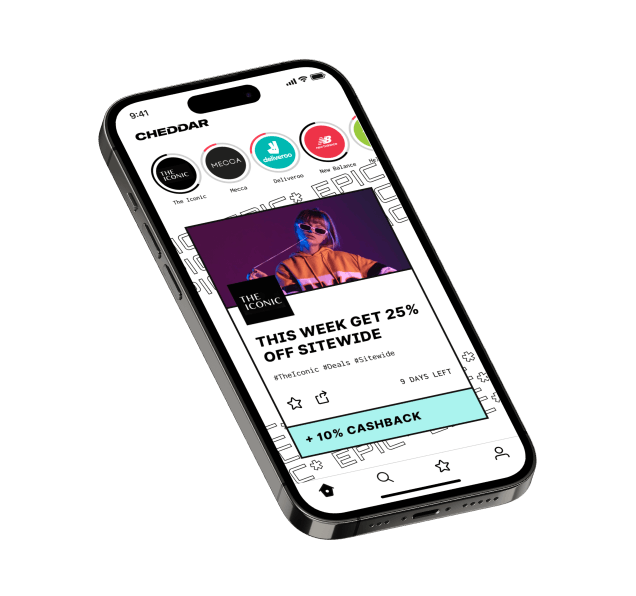

Cheddar was a deal discovery and cashback platform, launched to help young Australians get more back from their everyday spending.

Cheddar was a deal discovery and cashback platform, launched to help young Australians get more back from their everyday spending.
Cheddar
2021-2023
Everyday
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar
Cheddar


Cheddar was a deal discovery and cashback platform, launched to help young Australians get more back from their everyday spending.

Cheddar was a deal discovery and cashback platform, launched to help young Australians get more back from their everyday spending.
:Different
Closed 2023
Home
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
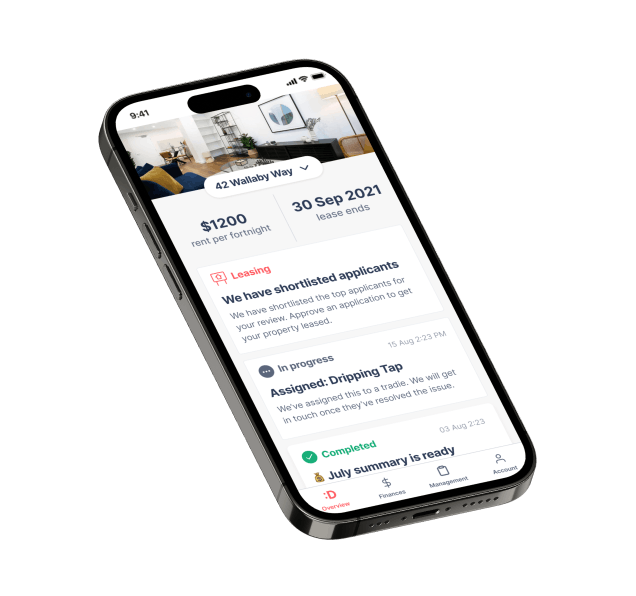

:Different removed friction from rental properties. For investors and tenants, this meant reliable property management, and for real estate agents, managing and scaling a profitable rent roll.

:Different removed friction from rental properties. For investors and tenants, this meant reliable property management, and for real estate agents, managing and scaling a profitable rent roll.
:Different
Closed 2023
Home
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different
:Different


:Different removed friction from rental properties. For investors and tenants, this meant reliable property management, and for real estate agents, managing and scaling a profitable rent roll.

:Different removed friction from rental properties. For investors and tenants, this meant reliable property management, and for real estate agents, managing and scaling a profitable rent roll.
© 2023 CBA New Digital Businesses Pty Ltd ABN 38 633 072 830 and Australian Credit Licence 516487, trading as x15ventures. x15ventures is a trade mark of CBA New Digital Businesses Pty Ltd. CBA New Digital Businesses Pty Ltd is a wholly owned but non-guaranteed subsidiary of the Commonwealth Bank of Australia ABN 48 123 123 124. CBA New Digital Businesses Pty Ltd is not an Authorised Deposit-taking Institution for the purposes of the Banking Act 1959 and its obligations do not represent deposits or other liabilities of Commonwealth Bank of Australia. Please refer to the venture websites for specific venture-related disclosures and other important information. Read our Privacy Policy.
© 2023 CBA New Digital Businesses Pty Ltd ABN 38 633 072 830 and Australian Credit Licence 516487, trading as x15ventures. x15ventures is a trade mark of CBA New Digital Businesses Pty Ltd. CBA New Digital Businesses Pty Ltd is a wholly owned but non-guaranteed subsidiary of the Commonwealth Bank of Australia ABN 48 123 123 124. CBA New Digital Businesses Pty Ltd is not an Authorised Deposit-taking Institution for the purposes of the Banking Act 1959 and its obligations do not represent deposits or other liabilities of Commonwealth Bank of Australia. Please refer to the venture websites for specific venture-related disclosures and other important information. Read our Privacy Policy.





